Bioproducts: Sustainable Solutions for a Greener Environment
Introduction
Bioproducts, derived from renewable resources, have emerged as a promising solution to address the environmental challenges associated with conventional products. These sustainable innovations encompass a wide range of materials, chemicals, and fuels that are produced using biomass, agricultural waste, or algae. This article delves into the different aspects of bioproducts, exploring their applications across industries, and the environmental benefits they offer.
Bioproducts
Bioproducts provide sustainable alternatives to conventional products. These innovations offer several environmental benefits, including reduced greenhouse gas emissions, decreased reliance on fossil fuels, and the promotion of a circular economy. Bioproducts have applications in various sectors, such as agriculture, energy, chemicals, materials, and consumer goods.
Bioproducts are manufactured using various production processes, including fermentation, pyrolysis, enzymatic conversion, and chemical synthesis. Fermentation involves the use of microorganisms or enzymes to convert biomass into valuable products such as biofuels, bioplastics, and renewable chemicals. Pyrolysis, on the other hand, uses heat to break down biomass into biochar, bio-oil, and syngas. Enzymatic conversion employs enzymes to catalyze biochemical reactions, enabling the production of bio-based materials and chemicals. Chemical synthesis utilizes renewable feedstocks as substitutes for fossil fuels in the production of traditional chemicals.
Here are some of the various types of bioproducts that are being developed and utilized in different industries:
Biofuels
Biofuels are a significant category of bioproducts that include ethanol, biodiesel, and biogas. Ethanol, derived from crops such as corn, sugarcane, or cellulosic biomass, is commonly used as a biofuel additive in gasoline. Biodiesel, produced from vegetable oils or animal fats, is used as a renewable substitute for diesel fuel. Biogas is generated through the anaerobic digestion of organic waste, such as agricultural residues or wastewater, and is used for heat and power generation.
The total global biofuel demand is estimated to increase by more than 20% between 2020 and 2027.

Bioplastics
Bioplastics are alternatives to traditional petroleum-based plastics, offering a more sustainable solution. They can be derived from renewable resources such as corn, sugarcane, or cellulose. Commonly available biodegradable bioplastics include Polylactic acid (PLA), Polybutadiene terephthalate (PBAT), Poly (hydroxyalkanoates) (PHA), and Poly (butylene succinate). When it comes to biodegradable polymers, PBAT, PLA, and their composites offer the finest performance and economic viability on the market today.
The yearly production of plastic exceeds 390 million tonnes, with bioplastics accounting for less than one percent. From about 2.23 million tonnes in 2022, global bioplastics production capacity is expected to expand to about 6.3 million tonnes in 2027.

Biofertilizers and Biostimulants
Biofertilizers and biostimulants are bioproducts used in agriculture to enhance crop productivity while reducing the reliance on synthetic fertilizers and chemicals. Biofertilizers contain beneficial microorganisms that enhance nutrient availability to plants, promote soil health, and improve nutrient uptake. Biostimulants, on the other hand, contain substances that stimulate plant growth, improve stress tolerance, and enhance overall plant health.
Biopesticides
Biopesticides are derived from natural materials or microorganisms and are used for pest management in agriculture. They provide an eco-friendly alternative to conventional chemical pesticides, reducing environmental contamination and minimizing health risks. Biopesticides include microbial-based pesticides, bio-insecticides, bio-fungicides, and bio-herbicides.
These are just a few examples of the diverse range of bioproducts being developed and utilized across industries. The field of bioproducts is constantly evolving, with ongoing research and innovations expanding the possibilities for sustainable alternatives in various sectors.
Applications across Industries
Bioproducts find applications across a wide range of industries, driving sustainable transformations. In the agriculture sector, biobased fertilizers, biopesticides, and biostimulants are being developed to enhance crop productivity while reducing the environmental impact of conventional agricultural practices. In the energy sector, biofuels such as ethanol, biodiesel, and biogas are replacing fossil fuels, thereby reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and promoting energy security. Bioplastics, derived from renewable resources, are increasingly used in packaging, automotive components, and consumer goods as sustainable alternatives to petroleum-based plastics. Renewable chemicals and materials, including bio-based solvents, polymers, and specialty chemicals, are finding applications in industries such as textiles, cosmetics, and construction.
Applications across Industries
The adoption of bioproducts offers several environmental benefits compared to their fossil fuel-based counterparts. By utilizing renewable feedstocks, bioproducts help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. The production of bioproducts often results in a smaller carbon footprint, as the renewable feedstocks absorb carbon dioxide during their growth phase. Furthermore, bioproducts contribute to the concept of a circular economy by utilizing waste or by-products from other industries as feedstock, reducing the overall environmental impact and promoting resource efficiency. Biodegradable bioproducts also offer a solution to the problem of plastic pollution, as they can be broken down naturally by biological processes.
Challenges
Despite the numerous benefits of bioproducts, there are still challenges that need to be addressed for their widespread adoption.
Few of the challenges associated with bioproducts are,
- Challenges related to feedstocks (cost, purity, variability)
- Catalyst issues (cost, high yield vs. selectivity, reactions to feedstock variability)
- Robust reactor design
- Risks associated with scale-up
- Process integration between biological and chemical methods
Technological advancements in biotechnology, synthetic biology, and sustainable chemistry will play a crucial role in overcoming these challenges. Collaboration between academia, industry, and governments is vital for driving research, development, and commercialization efforts. As the demand for sustainable alternatives continues to grow, the future of bioproducts looks promising, with the potential to revolutionize industries and contribute to a greener, more sustainable world.
Government Initiatives and Policies
India's bioeconomy is poised to touch 300 billion USD (US Dollar) by 2030. The Indian biotechnology market now accounts for less than 5% of the worldwide total. India plans to capture roughly 21% of the worldwide market by 2025, with a bio-economy worth USD 150 billion compared to the global projection of USD 725 billion in that time period.
The bioproducts are important part of the bioeconomy. The Indian government has implemented several initiatives and policies to support the development and adoption of bioproducts.
- National Policy on Biofuels: In 2018, India launched the National Policy on Biofuels, targeting a 20% ethanol blend in petrol by 2025 and D5 diesel by 2030.
- Plastic Waste Management Rules: The Government has introduced the Plastic Waste Management Rules to address the growing concern of plastic pollution. These rules emphasize the promotion of bioplastics and bio-based alternatives, encouraging their use in packaging and other sectors to reduce dependence on conventional plastics. Plastic Waste Management Amendment Rules, 2021, which prohibited the manufacture, import, stocking, distribution, sale, and use of single-use plastics (SUPs), intended to phase out the single-use Plastic Carry Bags of thickness less than 120 microns by December 2022.
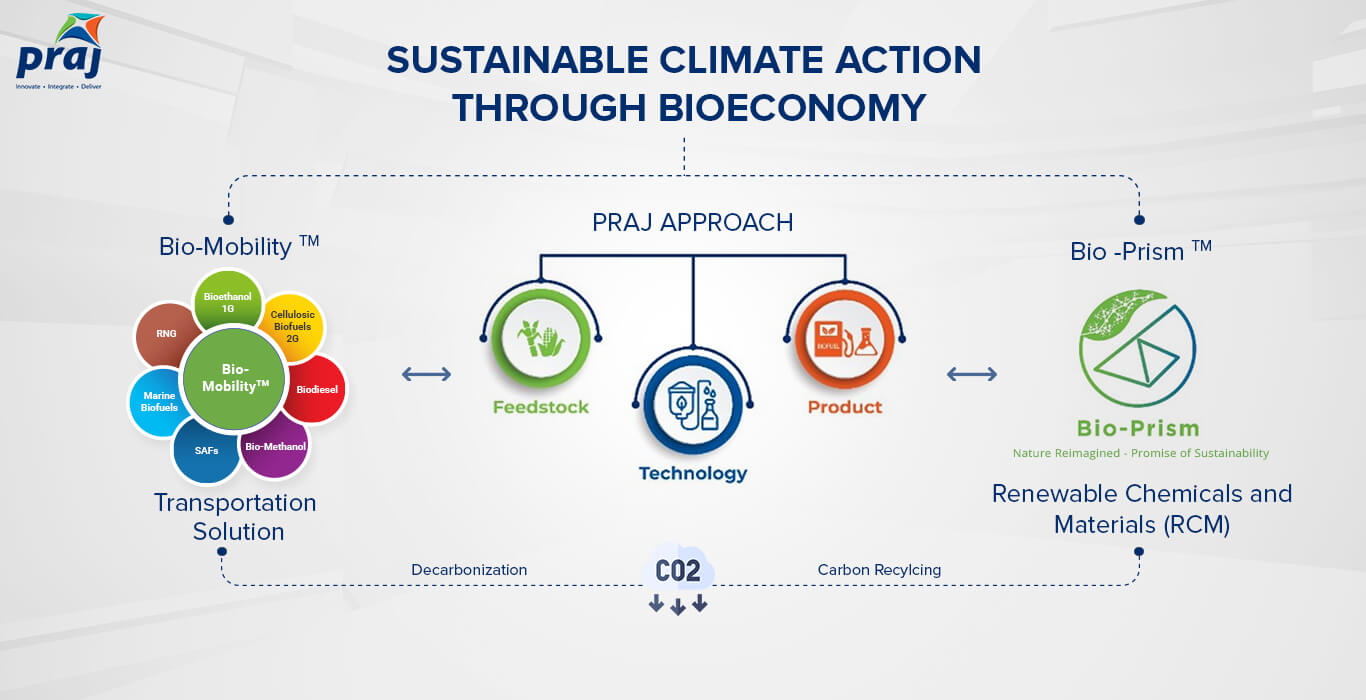
Praj at the forefront of bioeconomy
Praj is India's leading industrial biotech firm, driven by innovation, integration, and delivery capabilities. Praj's key contributions to the worldwide bioeconomy are the Bio-MobilityTM and Bio-PrismTM technologies. While the Bio-PrismTM portfolio includes technologies to produce renewable chemicals and materials, the Bio-MobilityTM platform provides technology solutions to produce renewable transportation fuel.

Bio-Prism™ portfolio
Praj’s Bio-PrismTM portfolio comprises a variety of bio-industrial products, including bioplastics as a priority, along with cellulose-lignin refinery products and specialty products. Praj has taken initiatives in the renewable chemicals space by developing multiple successful technologies like Furfural technology, leveraging lignin to obtain lignosulfonates and bio-bitumen. Lignosulfonates and Bio-bitumen are the only bio-based alternative for Asphalt/Bitumen used in cement and road construction.
Biopolymer, an important element in Renewable Chemicals and Materials (RCM), is produced from agricultural resources and can be used as a sustainable alternative to plastic. Praj is developing technologies for the production of Polylactic Acid (PLA), Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) & Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) bio-based polymers. Praj is also working with ICT Mumbai to set up a “Center of Excellence & Innovation” (CoEI) for Biopolymers.
Praj also presents an additional segment of bio-based specialty products including Hyaluronic acid, natural waxes, and antimicrobial peptides.
Conclusion
Bioproducts represent a sustainable pathway toward transforming industries and mitigating the environmental impacts of conventional products. These innovative solutions, produced from renewable resources, offer applications in agriculture, energy, chemicals, materials, and other sectors. By reducing greenhouse gas emissions, promoting resource efficiency, and tackling plastic pollution, bioproducts pave the way for a more sustainable future. Continued research, investment, and collaboration will be instrumental in furthering the development and adoption of bioproducts, driving positive change, and contributing to a more environmentally. Praj is continuously developing new technology innovations that are environment-friendly and making a huge impact on reducing the carbon footprint. With Praj’s advanced technologies, a wide portfolio of bio-based products can be produced that are sustainable alternatives to fossil-based products.
References:
- 1. https://dbtindia.gov.in/sites/default/files/NATIONAL%20BIOTECHNOLOGY%20DEVELOPMENT%20STRATEGY_01.04.pdf
- 2. https://www.iea.org/reports/renewables-2022/transport-biofuels
- 3. https://www.european-bioplastics.org/market/
- 4. https://biofuels-news.com/news/global-biofuel-demand-to-grow-20-in-next-five-years/
- 5. https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1902102
- 6. https://www.niti.gov.in/sites/default/files/2022-07/Plastics%20Alternative%20Study_Final_Report_compressed.pdf
- 7. https://www.agriculture.gov.au/sites/default/files/documents/december-2022-snapshot-of-global-biofuel-market.docx